
Introduction
PDFs have become a popular file format in our digital lives, serving a multitude of purposes. From academic assignments to professional documents, they’re a staple. However, managing large PDF files can often be cumbersome, requiring various online tools or applications.
As a student, I frequently encountered the challenge of converting handwritten notes into PDFs for submission. The process of splitting, merging, or rotating pages within these documents was often time-consuming and tedious. Recognizing this need, I decided to leverage my Python programming skills to create a more efficient solution.
This article will guide you through the process of building a versatile PDF editor using Python’s Tkinter library for a user-friendly interface and PyPDF2 for PDF file manipulation. With this tool, you’ll be able to:
- Split PDFs: Divide large documents into individual pages based on your specific requirements.
- Merge PDFs: Combine multiple files into a single, cohesive document.
- Rotate Pages: Easily adjust the orientation of pages within a PDF.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a powerful PDF editor tailored to your needs.
Requirement and Installation
Install the PyPDF2 library using the following command:
pip install PyPDF2
The Source Code
Create a new folder for your PDF editor and save a Python file named “pdf_editor.py” inside it.
Import the necessary modules
Let’s start writing your code by importing all the necessary modules.
import os import PyPDF2 import os.path from tkinter import * from functools import partial from tkinter import filedialog from PyPDF2 import PdfFileReader from tkinter import ttk, messagebox from PyPDF2.pdf import PdfFileWriter
Declare PDF Editor Class
Let’s create a class called “PDF_Editor.“ It will create a GUI window for us.
class PDF_Editor:
def __init__(self, root):
self.window = root
self.window.geometry("740x480")
self.window.title('PDF Editor')
# Color Options
self.color_1 = "white"
self.color_2 = "gray30"
self.color_3 = "black"
self.color_4 = 'orange red'
# Font Options
self.font_1 = "Helvetica"
self.font_2 = "Times New Roman"
self.font_3 = "Kokila"
self.saving_location = ''
# ================Menubar Section===============
self.menubar = Menu(self.window)
# Adding Edit Menu and its sub menus
edit = Menu(self.menubar, tearoff=0)
self.menubar.add_cascade(label='Edit', menu=edit)
edit.add_command(label='Split PDF',command=partial(self.SelectPDF, 1))
edit.add_command(label='Merge PDFs',command=self.Merge_PDFs_Data)
edit.add_separator()
edit.add_command(label='Rotate PDFs',command=partial(self.SelectPDF, 2))
# Adding About Menu
about = Menu(self.menubar, tearoff=0)
self.menubar.add_cascade(label='About', menu=about)
about.add_command(label='About', command=self.AboutWindow)
# Exit the Application
exit = Menu(self.menubar, tearoff=0)
self.menubar.add_cascade(label='Exit', menu=exit)
exit.add_command(label='Exit', command=self.Exit)
# Configuring the menubar
self.window.config(menu=self.menubar)
# ===================End=======================
# Creating a Frame
self.frame_1 = Frame(self.window,bg=self.color_2,width=740,height=480)
self.frame_1.place(x=0, y=0)
# Calling Home Page Window
self.Home_Page()
Implement the Home Window
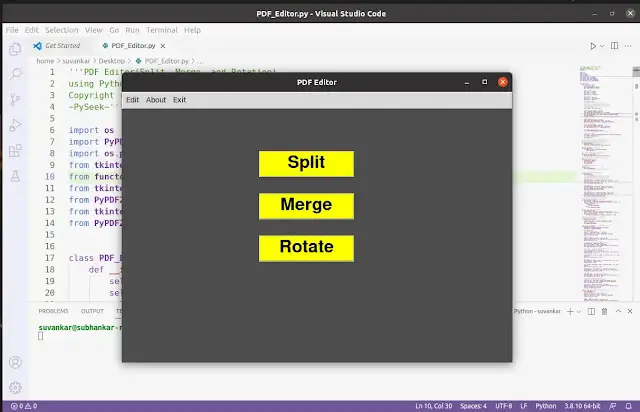
Let’s create the main screen for our PDF Editor. This screen will have three buttons: one for splitting PDFs, one for merging them, and one for rotating pages.
# Home Page: It consists Three Buttons
def Home_Page(self):
self.ClearScreen()
# ================Buttons Section===============
self.split_button = Button(self.frame_1, text='Split',
font=(self.font_1, 25, 'bold'), bg="yellow", fg="black", width=8,
command=partial(self.SelectPDF, 1))
self.split_button.place(x=260, y=80)
# Merge Button
self.merge_button = Button(self.frame_1, text='Merge',
font=(self.font_1, 25, 'bold'), bg="yellow", fg="black",
width=8, command=self.Merge_PDFs_Data)
self.merge_button.place(x=260, y=160)
# Merge Button
self.rotation_button = Button(self.frame_1, text='Rotate',
font=(self.font_1, 25, 'bold'), bg="yellow", fg="black",
width=8, command=partial(self.SelectPDF, 2))
self.rotation_button.place(x=260, y=240)
# ===================End=======================
Opening a single PDF file
Let’s create a method called ‘SelectPDF‘ to select and open a single PDF file using the Tkinter filedialog.
# Select the PDF for Splitting and Rotating
def SelectPDF(self, to_call):
self.PDF_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir = "/",
title = "Select a PDF File", filetypes = (("PDF files", "*.pdf*"),))
if len(self.PDF_path) != 0:
if to_call == 1:
self.Split_PDF_Data()
else:
self.Rotate_PDFs_Data()
Opening multiple PDF files
Let’s create another method to open multiple PDF files using the Tkinter filedialog.
# Select PDF files only for merging
def SelectPDF_Merge(self):
self.PDF_path = filedialog.askopenfilenames(initialdir = "/",
title = "Select PDF Files", filetypes = (("PDF files", "*.pdf*"),))
for path in self.PDF_path:
self.PDF_List.insert((self.PDF_path.index(path)+1), path)
Choose the saving location
Create a method named ‘select_directory‘ to choose the location where the resulting files will be stored.
# Select the directory where the result PDF
# file/files will be stored
def Select_Directory(self):
# Storing the 'saving location' for the result file
self.saving_location = filedialog.askdirectory(title =
"Select a location")
self.Update_Path_Label()
Get the data to split a PDF file
Our PDF editor allows users to choose one or more files to edit. Next, we’ll create a section where you can specify how you want to split the selected PDF(s). This includes setting the starting and ending page numbers, choosing a save location, and naming the resulting file. Once you’ve entered this information, simply click the ‘Split’ button to begin the process.
# Get the data from the user for splitting a PDF file
def Split_PDF_Data(self):
pdfReader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(self.PDF_path)
total_pages = pdfReader.numPages
self.ClearScreen()
# Button for getting back to the Home Page
home_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Home",
font=(self.font_1, 10, 'bold'), command=self.Home_Page)
home_btn.place(x=10, y=10)
# Header Label
header = Label(self.frame_1, text="Split PDF",
font=(self.font_3, 25, "bold"), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
header.place(x=265, y=15)
# Label for showing the total number of pages
self.pages_label = Label(self.frame_1,
text=f"Total Number of Pages: {total_pages}",
font=(self.font_2, 20, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
self.pages_label.place(x=40, y=70)
# From Label: the page number from where the
# user want to split the PDF pages
From = Label(self.frame_1, text="From",
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
From.place(x=40, y= 120)
self.From_Entry = Entry(self.frame_1, font=(self.font_2, 12, 'bold'),
width=8)
self.From_Entry.place(x=40, y= 160)
# To Label
To = Label(self.frame_1, text="To", font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'),
bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
To.place(x=160, y= 120)
self.To_Entry = Entry(self.frame_1, font=(self.font_2, 12, 'bold'),
width=8)
self.To_Entry.place(x=160, y= 160)
Cur_Directory = Label(self.frame_1, text="Storing Location",
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
Cur_Directory.place(x=300, y= 120)
# Constant
self.path_label = Label(self.frame_1, text='/',
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
self.path_label.place(x=300, y= 160)
# Button for selecting the directory
# where the splitted PDFs will be stored
select_loc_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Select Location",
font=(self.font_1, 8, 'bold'), command=self.Select_Directory)
select_loc_btn.place(x=320, y=200)
split_button = Button(self.frame_1, text="Split",
font=(self.font_3, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_4, fg=self.color_1,
width=12, command=self.Split_PDF)
split_button.place(x=250, y=250)
Get the data to merge multiple PDF files
In this section, you can specify details for merging multiple PDF files. A Tkinter listbox is provided to display the PDFs selected for merging.
For added flexibility, users can easily add more PDFs to the list or remove specific ones as needed.
# Get the data from the user for Merge PDF files
def Merge_PDFs_Data(self):
self.ClearScreen()
# Button for get back to the Home Page
home_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Home",
font=(self.font_1, 10, 'bold'), command=self.Home_Page)
home_btn.place(x=10, y=10)
# Header Label
header = Label(self.frame_1, text="Merge PDFs",
font=(self.font_3, 25, "bold"), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
header.place(x=265, y=15)
select_pdf_label = Label(self.frame_1, text="Select PDFs",
font=(self.font_2, 20, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
select_pdf_label.place(x=40, y=70)
open_button = Button(self.frame_1, text="Open Folder",
font=(self.font_1, 9, 'bold'), command=self.SelectPDF_Merge)
open_button.place(x=55, y=110)
Cur_Directory = Label(self.frame_1, text="Storing Location",
font=(self.font_2, 18, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
Cur_Directory.place(x=40, y= 150)
# Constant
self.path_label = Label(self.frame_1, text='/',
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
self.path_label.place(x=40, y= 190)
# Button for selecting the directory
# where the merged PDFs will be stored
select_loc_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Select Location",
font=(self.font_1, 9, 'bold'), command=self.Select_Directory)
select_loc_btn.place(x=55, y=225)
saving_name = Label(self.frame_1, text="Choose a Name",
font=(self.font_2, 18, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
saving_name.place(x=40, y=270)
# Get the 'result file' name from the user
self.sv_name_entry = Entry(self.frame_1,
font=(self.font_2, 12, 'bold'), width=20)
self.sv_name_entry.insert(0, 'Result')
self.sv_name_entry.place(x=40, y=310)
merge_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Merge",
font=(self.font_1, 10, 'bold'), command=self.Merge_PDFs)
merge_btn.place(x=80, y=350)
listbox_label = Label(self.frame_1, text="Selected PDFs",
font=(self.font_2, 18, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
listbox_label.place(x=482, y=72)
# Listbox for showing the selected PDF files
self.PDF_List = Listbox(self.frame_1,width=40, height=15)
self.PDF_List.place(x=400, y=110)
delete_button = Button(self.frame_1, text="Delete",
font=(self.font_1, 9, 'bold'), command=self.Delete_from_ListBox)
delete_button.place(x=400, y=395)
more_button = Button(self.frame_1, text="Select More",
font=(self.font_1, 9, 'bold'), command=self.SelectPDF_Merge)
more_button.place(x=480, y=395)
Specify the pages you want to rotate within the PDF file
Similar to the previous methods, you’ll need to provide details for rotating pages within the PDF. Specify the page numbers you want to rotate.
# Get the data from the user for Rotating one/multiple
# pages of a PDF file
def Rotate_PDFs_Data(self):
self.ClearScreen()
pdfReader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(self.PDF_path)
total_pages = pdfReader.numPages
# Button for get back to the Home Page
home_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Home",
font=(self.font_1, 10, 'bold'), command=self.Home_Page)
home_btn.place(x=10, y=10)
# Header Label
header = Label(self.frame_1, text="Rotate PDFs",
font=(self.font_3, 25, "bold"), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
header.place(x=265, y=15)
# Label for showing the total number of pages
self.pages_label = Label(self.frame_1,
text=f"Total Number of Pages: {total_pages}",
font=(self.font_2, 20, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
self.pages_label.place(x=40, y=90)
Cur_Directory = Label(self.frame_1, text="Storing Location",
font=(self.font_2, 18, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
Cur_Directory.place(x=40, y= 150)
self.fix_label = Label(self.frame_1,
text="Rotate this Pages(Comma-Separated-Number)",
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
self.fix_label.place(x=260, y= 150)
self.fix_entry = Entry(self.frame_1,
font=(self.font_2, 12, 'bold'), width=40)
self.fix_entry.place(x=260, y=190)
# Constant
self.path_label = Label(self.frame_1, text='/',
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_3)
self.path_label.place(x=40, y= 190)
# Button for selecting the directory
# where the rotated PDFs will be stored
select_loc_btn = Button(self.frame_1, text="Select Location",
font=(self.font_1, 9, 'bold'), command=self.Select_Directory)
select_loc_btn.place(x=55, y=225)
saving_name = Label(self.frame_1, text="Choose a Name",
font=(self.font_2, 18, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
saving_name.place(x=40, y=270)
# Get the 'result file' name from the user
self.sv_name_entry = Entry(self.frame_1,
font=(self.font_2, 12, 'bold'), width=20)
self.sv_name_entry.insert(0, 'Result')
self.sv_name_entry.place(x=40, y=310)
which_side = Label(self.frame_1, text="Rotation Alignment",
font=(self.font_2, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_2, fg=self.color_1)
which_side.place(x=260, y=230)
# Rotation Alignment(Clockwise and Anti-Clockwise)
text = StringVar()
self.alignment = ttk.Combobox(self.frame_1, textvariable=text)
self.alignment['values'] = ('ClockWise',
'Anti-ClockWise'
)
self.alignment.place(x=260, y=270)
rotate_button = Button(self.frame_1, text="Rotate",
font=(self.font_3, 16, 'bold'), bg=self.color_4,
fg=self.color_1, width=12, command=self.Rotate_PDFs)
rotate_button.place(x=255, y=360)
Perform the split operation
This method is called when the ‘Split‘ button is clicked. It performs the core operation of splitting a PDF file into smaller parts using the PyPDF2 library.
# It manages the task for Splitting the
# selected PDF file
def Split_PDF(self):
if self.From_Entry.get() == "" and self.To_Entry.get() == "":
messagebox.showwarning("Warning!",
"Please mention the page rangen you want to split")
else:
from_page = int(self.From_Entry.get()) - 1
to_page = int(self.To_Entry.get())
pdfReader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(self.PDF_path)
for page in range(from_page, to_page):
pdfWriter = PdfFileWriter()
pdfWriter.addPage(pdfReader.getPage(page))
splitPage = os.path.join(self.saving_location,f'{page+1}.pdf')
resultPdf = open(splitPage, 'wb')
pdfWriter.write(resultPdf)
resultPdf.close()
messagebox.showinfo("Success!","The PDF file has been splitted")
self.saving_location = ''
self.total_pages = 0
self.ClearScreen()
self.Home_Page()
Perform the merge Operation
Let’s define a method named ‘Merge_PDFs‘ to perform the merge operation of multiple PDF files.
# It manages the task for Merging the
# selected PDF files
def Merge_PDFs(self):
if len(self.PDF_path) == 0:
messagebox.showerror("Error!", "Please Select PDFs first")
else:
if self.saving_location == '':
curDirectory = os.getcwd()
else:
curDirectory = str(self.saving_location)
presentFiles = list()
for file in os.listdir(curDirectory):
presentFiles.append(file)
checkFile = f'{self.sv_name_entry.get()}.pdf'
if checkFile in presentFiles:
messagebox.showwarning('Warning!',
"Please select an another file name to saved")
else:
pdfWriter = PyPDF2.PdfFileWriter()
for file in self.PDF_path:
pdfReader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(file)
numPages = pdfReader.numPages
for page in range(numPages):
pdfWriter.addPage(pdfReader.getPage(page))
mergePage = os.path.join(self.saving_location,
f'{self.sv_name_entry.get()}.pdf')
mergePdf = open(mergePage, 'wb')
pdfWriter.write(mergePdf)
mergePdf.close()
messagebox.showinfo("Success!",
"The PDFs have been merged successfully")
self.saving_location = ''
self.ClearScreen()
self.Home_Page()
Delete items from the listbox
Earlier, we discussed how users could remove a selected PDF from the listbox when merging files. Now, let’s create a dedicated method to handle this action.
# Delete an item(One PDF Path)
def Delete_from_ListBox(self):
try:
if len(self.PDF_path) < 1:
messagebox.showwarning('Warning!',
'There is no more files to delete')
else:
for item in self.PDF_List.curselection():
self.PDF_List.delete(item)
self.PDF_path = list(self.PDF_path)
del self.PDF_path[item]
except Exception:
messagebox.showwarning('Warning!',"Please select PDFs first")
Perform the rotation operation
This method will rotate the selected pages clockwise or counterclockwise, depending on your choice.
# It manages the task for Rotating the pages/page of
# the selected PDF file
def Rotate_PDFs(self):
need_to_fix = list()
if self.fix_entry.get() == "":
messagebox.showwarning("Warning!",
"Please enter the page number separated by comma")
else:
for page in self.fix_entry.get().split(','):
need_to_fix.append(int(page))
if self.saving_location == '':
curDirectory = os.getcwd()
else:
curDirectory = str(self.saving_location)
presentFiles = list()
for file in os.listdir(curDirectory):
presentFiles.append(file)
checkFile = f'{self.sv_name_entry.get()}.pdf'
if checkFile in presentFiles:
messagebox.showwarning('Warning!',
"Please select an another file name to saved")
else:
if self.alignment.get() == 'ClockWise':
pdfReader = PdfFileReader(self.PDF_path)
pdfWriter = PdfFileWriter()
rotatefile = os.path.join(self.saving_location,
f'{self.sv_name_entry.get()}.pdf')
fixed_file = open(rotatefile, 'wb')
for page in range(pdfReader.getNumPages()):
thePage = pdfReader.getPage(page)
if (page+1) in need_to_fix:
thePage.rotateClockwise(90)
pdfWriter.addPage(thePage)
pdfWriter.write(fixed_file)
fixed_file.close()
messagebox.showinfo('Success', 'Rotation Complete')
self.Update_Rotate_Page()
elif self.alignment.get() == 'Anti-ClockWise':
pdfReader = PdfFileReader(self.PDF_path)
pdfWriter = PdfFileWriter()
rotatefile = os.path.join(self.saving_location,
f'{self.sv_name_entry.get()}.pdf')
fixed_file = open(rotatefile, 'wb')
for page in range(pdfReader.getNumPages()):
thePage = pdfReader.getPage(page)
if (page+1) in need_to_fix:
thePage.rotateCounterClockwise(90)
pdfWriter.addPage(thePage)
pdfWriter.write(fixed_file)
fixed_file.close()
messagebox.showinfo('Success','Rotation Complete')
self.Update_Rotate_Page()
else:
messagebox.showwarning('Warning!',
"Please Select a Right Alignment")
Initialize the application
In the main part of your code, create an instance of the ‘PDF_Editor‘ class to build the GUI, and then start the main loop.
# The main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
# Creating a CountDown class object
obj = PDF_Editor(root)
root.mainloop()
In this block of code, we check if the script is being run as the main program (__name__ == “__main__”). This ensures that the code inside this block only runs when the script is executed, not when it’s imported as a module.
Output
Summary
In this tutorial, we’ve built a practical PDF editor using Python’s Tkinter and PyPDF2 libraries. This tool allows you to split, merge, and rotate PDF files with ease. We’ve prioritized user-friendliness throughout the development process.
I encourage you to try out this PDF editor and share your feedback in the comments. For more Python Tkinter projects and examples, visit our dedicated page: Python Projects. Here are a few examples to spark your interest:
Happy Editing!






