Garbage is a serious problem for our society and environment. That’s why garbage detection is becoming important as we look to keep our environment clean and safe. From public spaces to private properties, detecting and removing waste is crucial in maintaining hygiene and reducing pollution.
However, monitoring waste in large areas manually can be challenging and time-consuming. This is where deep learning models like YOLO (You Only Look Once) come into play, enabling real-time garbage detection in images and videos.
In this article, we’ll walk through a Python project that uses the YOLOv8 object detection model to detect garbage in images and live videos. We’ll explore how computer vision techniques with OpenCV and YOLO can simplify the garbage detection process.
This project involves two Python programs: one for detecting garbage in images and another for detecting garbage in videos in real-time.
Let’s dive into the details!
Requirements and Installations
Before we start coding, let’s ensure Python (3.6 or later) is installed on your computer. If you don’t have Python, you can download it for free from https://www.python.org/downloads/.
Now download all the dependencies we require using the following commands:
pip install gitpython>=3.1.30 pip install matplotlib>=3.3 pip install numpy>=1.23.5 pip install opencv-python>=4.1.1 pip install pillow>=10.3.0 pip install psutil pip install PyYAML>=5.3.1 pip install requests>=2.32.0 pip install scipy>=1.4.1 pip install thop>=0.1.1 pip install torch>=1.8.0 pip install torchvision>=0.9.0 pip install tqdm>=4.64.0 pip install ultralytics>=8.2.34 pip install pandas>=1.1.4 pip install seaborn>=0.11.0 pip install setuptools>=65.5.1 pip install filterpy pip install scikit-image pip install lap
Alternative Installation
Installing the above utilities one by one might be a boring task. Instead, you can download the ‘requirements.txt‘ file containing all the dependencies above. Just run the following command. It will automate the whole task in one go.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Training of YOLO Model on Custom Dataset
At the very first, we have to train our YOLO model on the custom dataset. Please follow the steps below:
Download the Dataset
Download the garbage detection dataset from roboflow.com.
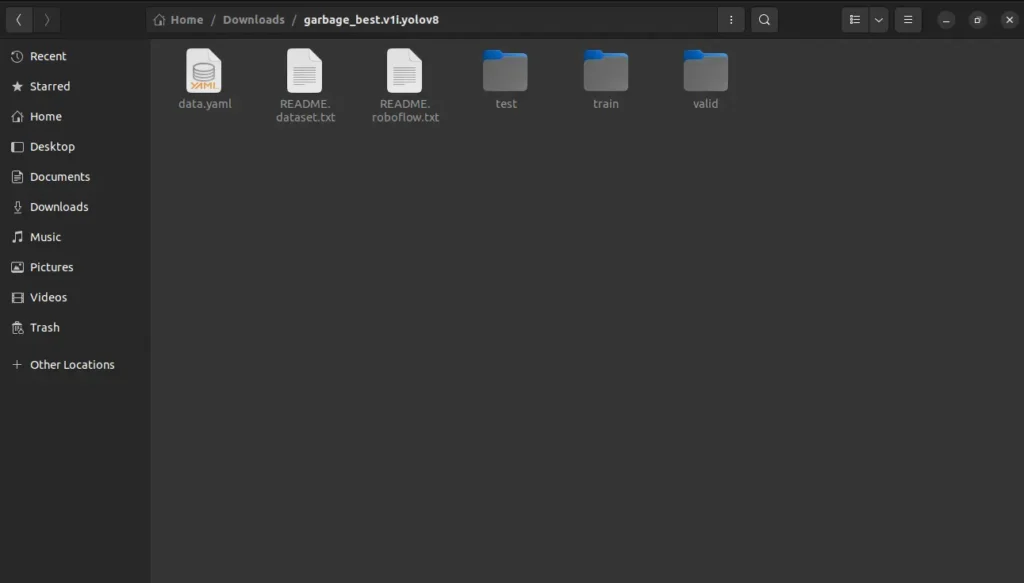
Now unzip the downloaded dataset. The folder should look like the following:
Training YOLOv8 Model with Custom Dataset using Colab
Open Google Colab, sign in with your Gmail account and open a new notebook.
Now go to the ‘Runtime‘ menu, select ‘Change runtime type‘, choose ‘T4 GPU‘ for the Hardware accelerator, and save it.
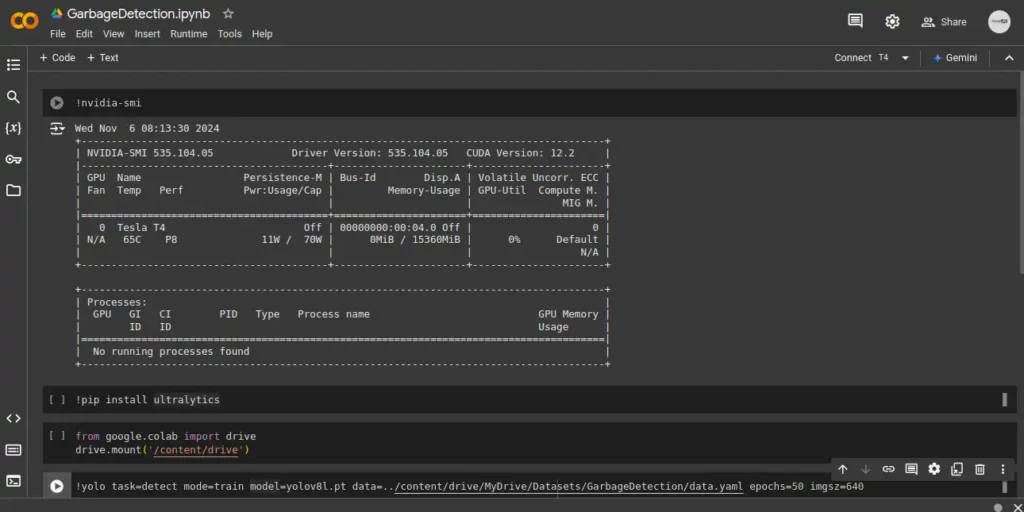
Let’s check whether the GPU is running perfectly or not using the following command:
!nvidia-smi
The output should look like the following:
Next, install ultralytics on your colab workspace using the following command:
!pip install ultralytics
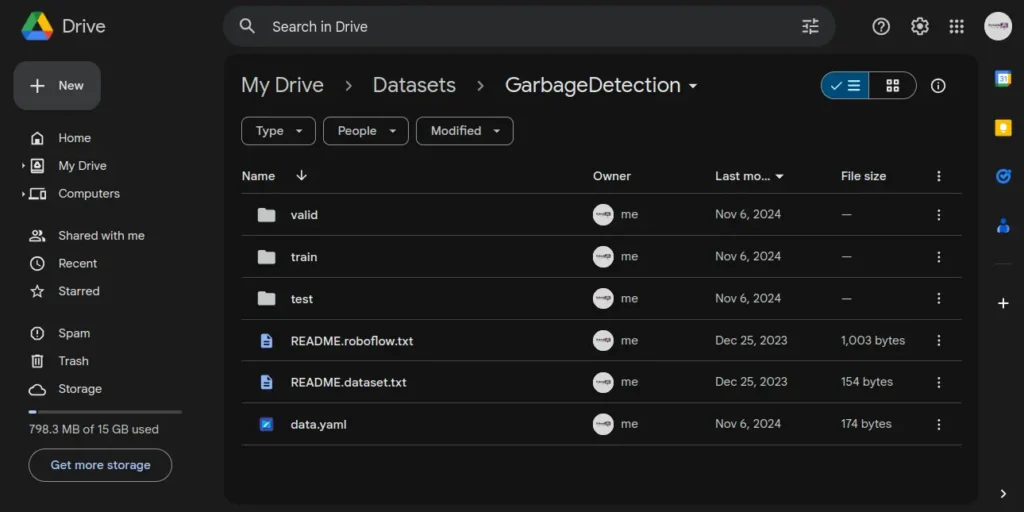
Now open your Google Drive and navigate to ‘My Drive.’ Now create a folder named ‘Datasets‘ under ‘My Drive’ and inside the ‘Datasets’ folder create one more folder ‘GarbageDetection.’
Let’s open the unzipped dataset folder, select all items present there, and drop them into the ‘GarbageDetection’ folder on Google Drive. It may take a while so wait until it is finished. The final ‘GarbageDetection’ folder will look like the following:
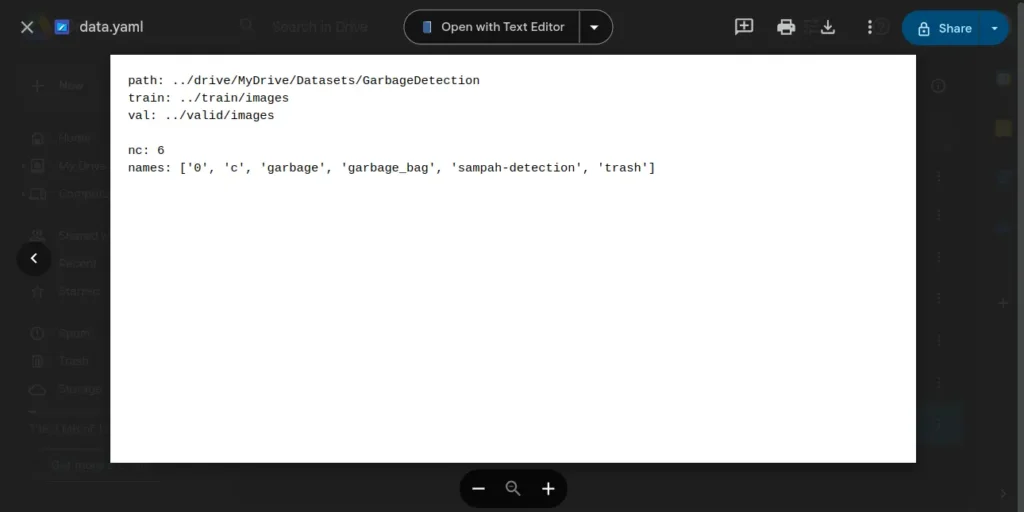
Now open the ‘data.yaml‘ file in the text editor and modify the path variable to: “../drive/MyDrive/Datasets/GarbageDetection” The final ‘data.yaml‘ file will look like the following:
Now, let’s go back to our Google Colab dashboard. You need to mount your Google Drive with the Colab. Insert the following command in a new cell and run it:
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')You should get a success message like this: “Drive already mounted at /content/drive; to attempt to forcibly remount, call drive.mount(“/content/drive”, force_remount=True).”
Now we will start training our YOLO model with our garbage detection dataset. Again, create a new cell, insert the command below, and run it.
!yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8l.pt data=../content/drive/MyDrive/Datasets/GarbageDetection/data.yaml epochs=50 imgsz=640
Here, ‘epochs=50‘ specifies the number of training epochs. An epoch is one complete pass through the entire training dataset. Here, the model will be trained for 50 epochs.
‘imgsz=640‘ sets the size of the input images on which the model will be trained. In this case, images will be resized to 640×640 pixels before being fed into the model.
The whole training can take around 1 – 2 hours even more to complete.
After, the completion of the training go to the ‘Files‘ section in your Colab dashboard and navigate through these folders: ‘runs’ -> ‘detect’ -> ‘train’ -> ‘weights’. Inside the ‘weights‘ folder you will see ‘best.pt‘ and ‘last.pt‘ these two files. Download ‘best.pt‘ from there.
Setting Up the Environment
For this project, create a folder named “GarbageDetector” on your computer. Under this folder, create two more folders named ‘Weights‘ and ‘Media‘ to store pre-trained YOLO models and images, respectively.
Place the Downloaded YOLO Model
In the previous section, we trained our YOLO model with a custom garbage detection dataset and downloaded a file named ‘best.pt.’ Now place that file inside the ‘Weights’ folder.
Media Files
I have collected suitable images from the Internet for this project and recorded real video footage of garbage on the road. These media files will help you check the project’s execution.
You can get those using the ‘Download‘ button below. All you have to do is, download the zip file, unzip it, and place those images inside the ‘Media‘ folder.
Create Your Python Script
We’re almost at the end of setting up the environment. Now choose your favorite text editor and open the entire project folder ‘GarbageDetector.’ Inside this folder, create a Python program file named ‘GarbageDetector.py.‘ This is where you’ll write the code.
Your final project file hierarchy should look like the following:
GarbageDetector/ ├── Weights/ │ └── best.pt ├── Media/ │ └── garbage_1.jpg │ └── garbage_2.jpg │ └── garbage_3.jpeg │ └── garbage_4.jpg │ └── garbage_5.jpeg │ └── garbage.mp4 ├── GarbageDetector.py ├── GarbageDetectorLive.py
The Program – Garbage Detection from Images
First, we will create a Python program to detect garbage only in images. Let’s start writing your code step-by-step and try to understand the logic.
Import Libraries
First, we need to import the necessary libraries. Here, ‘OpenCV‘ is used for image processing, ‘cvzone‘ helps draw bounding boxes, and ‘YOLO’ from the ‘ultralytics‘ library is used for object detection.
import cv2 import math import cvzone from ultralytics import YOLO
Load YOLO Model and Define Class Names
Next, load the YOLO model with the custom-trained weights and define the class names that YOLO can detect. Make sure you have downloaded the ‘best.pt‘ weights and placed them in the correct directory.
# Load YOLO model with custom weights
yolo_model = YOLO("Weights/best.pt")
# Define class names
class_labels = ['0', 'c', 'garbage', 'garbage_bag', 'sampah-detection', 'trash']Load the Image
Now, load the image you want to process using OpenCV’s ‘imread‘ method.
# Load the image image_path = "Media/garbage_1.jpg" img = cv2.imread(image_path)
Perform Object Detection
Now use ‘yolo_model‘ to detect objects in the loaded image.
# Perform object detection results = yolo_model(img)
Draw Bounding Boxes and Labels
Now we will loop through the detected objects and draw bounding boxes around them. The confidence score and class label will also be displayed.
# Loop through the detections and draw bounding boxes
for r in results:
boxes = r.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
conf = math.ceil((box.conf[0] * 100)) / 100
cls = int(box.cls[0])
if conf > 0.3:
cvzone.cornerRect(img, (x1, y1, w, h), t=2)
cvzone.putTextRect(img, f'{class_labels[cls]} {conf}', (x1, y1 - 10), scale=0.8, thickness=1, colorR=(255, 0, 0))Display the Image
Finally, we will display the processed image using OpenCV’s ‘imshow‘ method. The window will close when the ‘q‘ button is pressed.
# Display the image with detections
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
# Close window when 'q' button is pressed
while True:
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.waitKey(1)Output
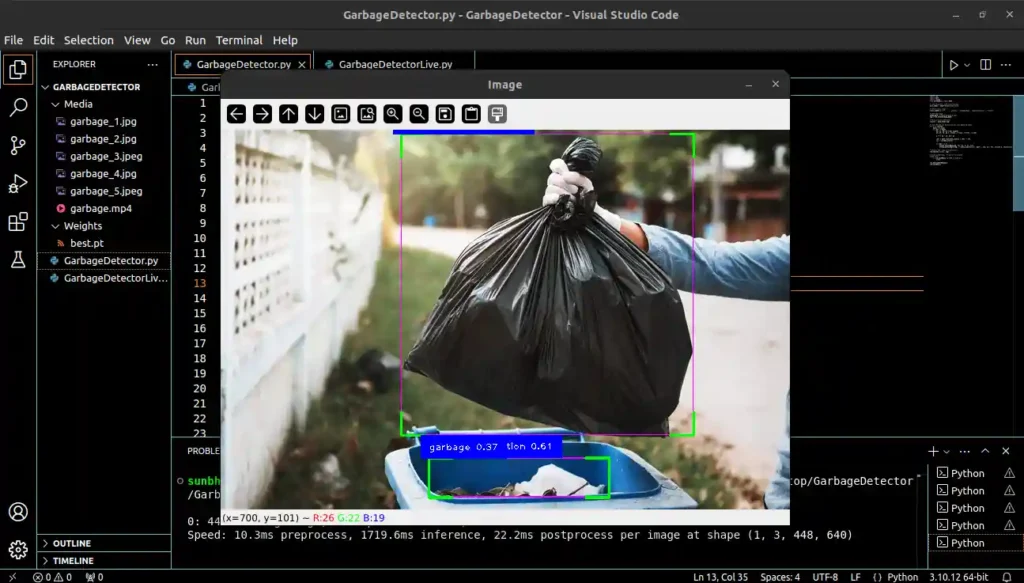
Output 1
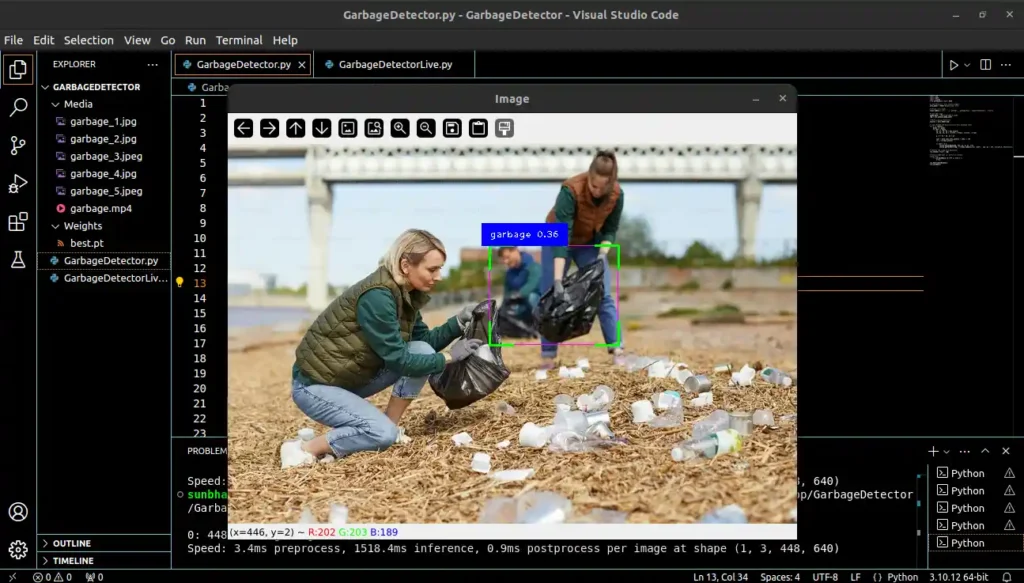
Output 2
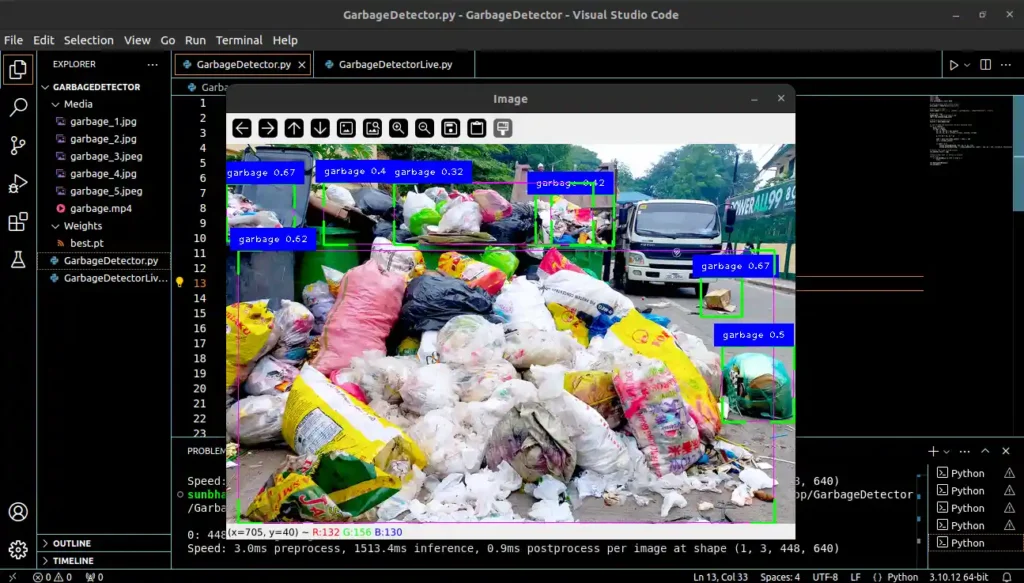
Output 3
Output 4
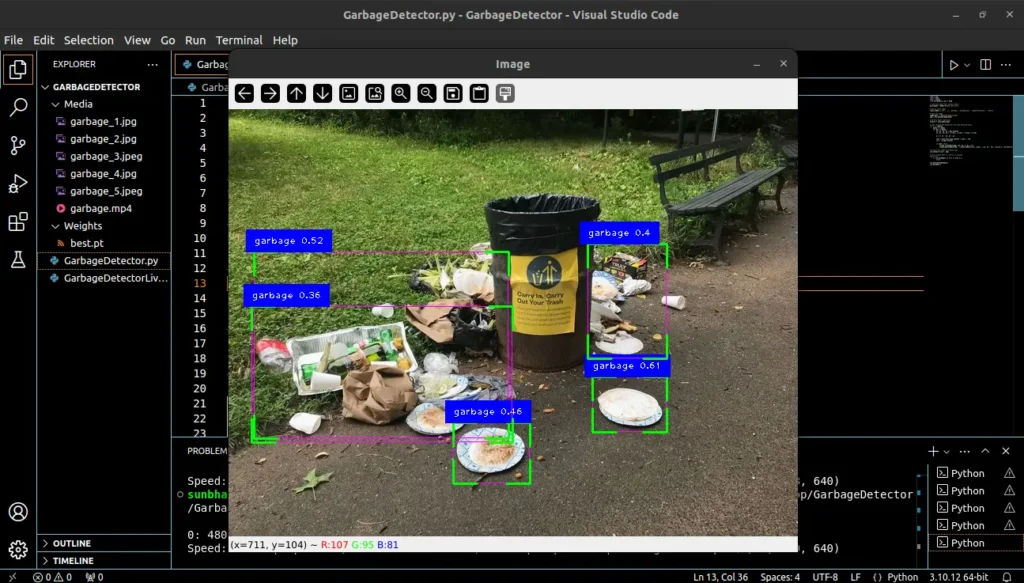
The Program – Garbage Detection in Videos (Real-Time)
In the previous section, we developed a Python program that detects garbage in images. Now, we’ll explore a different program for live garbage detection in a video.
This program closely resembles the previous one, but here, we’ll use the ‘cv2.VideoCapture()‘ function to capture video frames and a while loop to process them continuously.
Here is the program:
import cv2
import math
import cvzone
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Initialize video capture
video_path = "Media/garbage.mp4"
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# Load YOLO model with custom weights
model = YOLO("Weights/best.pt")
# Define class names
classNames = ['0', 'c', 'garbage', 'garbage_bag', 'sampah-detection', 'trash']
while True:
success, img = cap.read()
results = model(img, stream=True)
for r in results:
boxes = r.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
conf = math.ceil((box.conf[0] * 100)) / 100
cls = int(box.cls[0])
if conf > 0.1:
cvzone.cornerRect(img, (x1, y1, w, h), t=2)
cvzone.putTextRect(img, f'{classNames[cls]} {conf}', (max(0, x1), max(35, y1)), scale=1, thickness=1)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
breakOutput
Summary
Garbage detection is essential for keeping our environment clean and improving waste management processes. This project demonstrated how to create a Python-based garbage detection system using YOLO and OpenCV. We explored two versions: one that detects garbage in a single image and another that enables real-time video detection.
This project highlights the power of computer vision and deep learning for environmental monitoring and provides a foundation for developing more sophisticated waste management systems.
Recommended Article: Detecting Potholes on Roads Using Python and YOLOv8
For any query related to this project, reach out to me at contact@pyseek.com.
Happy Coding!